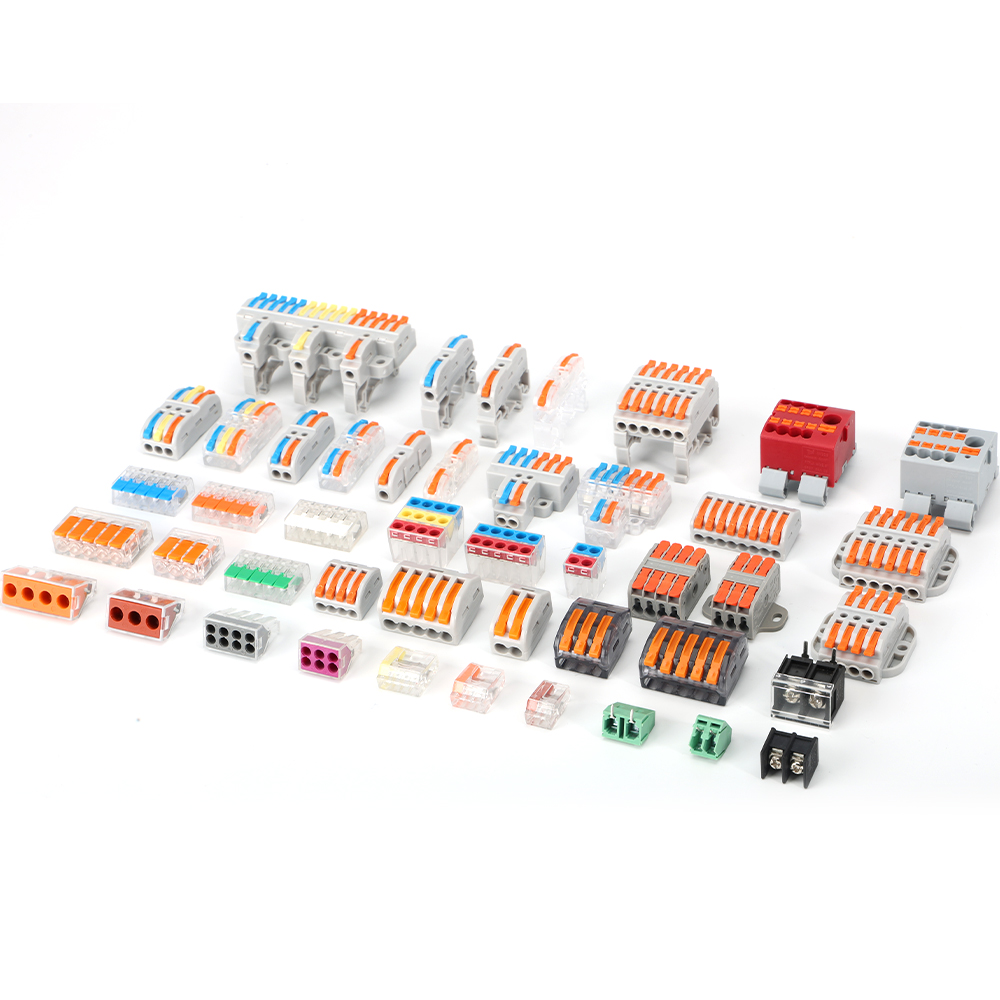
Rail-mounted terminal blocks, with their modularity, standardization, and ease of installation, have become an indispensable core component in control cabinets, distribution boxes, and other equipment. This article will delve into what are rail-mounted terminal blocks, their wide applications, working principles, and correct wiring methods.
What Is Rail-Mounted Terminal Blocks
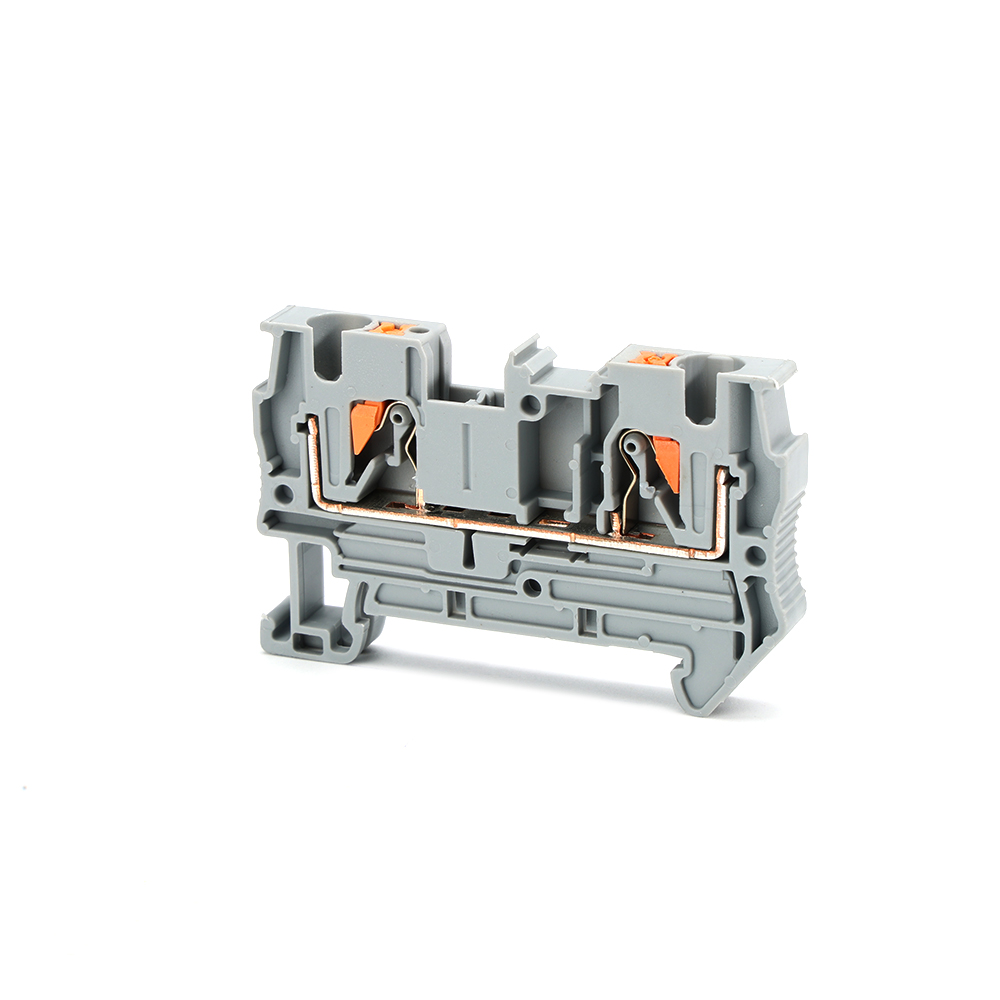
DIN rail terminal blocks, also known as terminal blocks or wiring strips, are modular components used for connecting and branching electrical circuits. Their core feature is their ability to be securely mounted on standardised DIN rails via a simple snap-fit mechanism.
A typical terminal block usually consists of the following components:
Insulating housing: Typically made of flame-retardant engineering plastics (such as nylon PA66), providing electrical insulation and protection.
Conductive component: Usually a metal (such as a copper alloy) clamping element and conductor, responsible for current transmission.
Clamping mechanism: Includes screws, springs, clamps, etc., used to secure and clamp the wires.
Snap-fit/DIN rail mounting slot: Used to quickly attach the terminal to the DIN rail.
They can be used individually, but more commonly, multiple terminals with the same or different functions are mounted side-by-side on a rail to form a “terminal block” for organising, distributing, and connecting complex circuits.
What Are Terminal Blocks Used For
Rail-mounted terminal blocks have a wide range of applications, covering almost all situations requiring centralized wiring and circuit connections.
Industrial Automation And Plc Control System
In automated production lines and PLC control cabinets, numerous sensors, actuators, relays, and controllers require connection. Terminal blocks, serving as central connection points, provide a clear and orderly connection scheme for PLC input/output signals and power distribution, greatly facilitating debugging, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
Power Distribution System (Such As Distribution Cabinets)
In electrical distribution cabinets in buildings and factories, terminal blocks are used for the introduction of main power, the distribution of branch circuits, and the isolation between circuits of different voltage levels. Dedicated grounding terminals, fuse terminals, etc., also provide safety protection functions.
Mechanical Equipment Manufacturing
Various CNC machine tools, packaging machinery, textile machinery, etc., all require the use of terminal blocks inside their electrical control boxes to connect components such as motors, drivers, buttons, and indicator lights, in order to achieve neat and standardized wiring inside the equipment.
How Do Terminal Blocks Work
The working principle of terminal blocks is very simple and straightforward; their core function is to provide a safe and reliable “electrical relay station.”
Physical Connection: By tightening screws (or other clamping methods, such as spring connections), the metal conductor of a wire is firmly pressed against the conductive element of the terminal.
Current Transmission: Current flows in from one wire, passes through the metal conductive element inside the terminal, and is then transmitted to the wire on the other side or to an adjacent terminal.
Circuit Distribution and Busing: Multiple terminals arranged together can be electrically connected using bridging elements (short-circuit elements), thereby enabling one input signal to be distributed to multiple outputs, or multiple input signals to be combined into one output.
The entire process is carried out under the protection of an insulating housing, effectively preventing short circuits and the risk of electric shock.
How To Wire A Terminal Block Strip
Proper installation and wiring are key to ensuring the long-term stable operation of terminal blocks.
Planning And Selection
Layout Planning: Based on the circuit diagram, plan the type, quantity, and arrangement order of terminal blocks. For example, separate power terminals and signal terminals, leaving gaps in between or using isolation terminals.
Selection: Choose appropriate terminal models based on current, voltage level, and conductor cross-sectional area. Also consider whether special function terminals are needed, such as fuse terminals, diode terminals, or switch terminals.
Installation Onto Din Rail
Open the clips at the bottom (or top) of the terminal block.
First, hook the top clip of the terminal block onto the upper edge of the DIN rail.
Gently press down until the bottom clip of the terminal block clicks into place on the lower edge of the rail, completing the installation. To remove, simply pry open the bottom clip with a screwdriver and lift it upwards to remove the terminal block.
Terminal Wiring
Preparation: Use wire strippers to strip the insulation of the wire to a suitable length (usually 10-12mm), avoiding exposing too much or too little insulation.
Loosen the screw: Using a suitable screwdriver (usually Phillips or flathead), loosen the terminal screw counterclockwise.
Insert the wire: Insert the exposed wire straight into the deepest part of the terminal hole, ensuring all copper wires are in the clamping area.
Tighten the screw: Tighten the screw clockwise, applying appropriate torque to firmly clamp the wire. Note: Do not apply excessive torque, as this may damage the wire or threads.
Check: Gently pull the wire to confirm it is securely clamped and not loose.
Labeling: Use terminal markings or labels to clearly identify the function of each terminal for easy maintenance in the future.
6. FAQ:
What Is Din Rail?
DIN rails are standardized metal rails with a “hat” or “G” shaped cross-section, hence they are often called “hat-shaped rails.” Originating from German industrial standards, they have become a globally accepted installation standard. Electrical components (such as terminals, circuit breakers, and contactors) can be quickly and neatly installed on them.
Why Use Din Rail Mounted Terminal Blocks?
Key advantages include:
Modular and flexible: Can be freely combined and expanded as needed, easy to modify and upgrade.
Easy installation: Quickly snaps onto DIN rails, saving installation time.
Neat and aesthetically pleasing: Keeps wiring within the control cabinet organized and enhances professionalism.
Easy maintenance: Clear wiring, easy location and repair of fault points.
Safe and reliable: Insulated housing provides protection against accidental electric shock and short circuits.
Is It Safe To Use Terminal Blocks In Residential Wiring?
In residential fixed wiring (such as concealed wiring within walls), DIN rail terminal blocks are generally not recommended as the primary connection method. The standard practice is to use junction boxes with soldered, wire nut, or lever-type connectors like WAGO, ensuring the junction boxes are easily accessible for maintenance.
DIN rail terminal blocks are more commonly used inside distribution boxes, control cabinets, and other similar equipment. If temporary use is necessary in a residential environment, ensure they are installed in an IP-rated enclosure and handled by a qualified electrician to protect against dust, moisture, and electric shock.
7. Conclusion
Rail-mounted terminal blocks, through standardized design, transform messy wiring into an orderly and manageable connection system, and are widely used in industrial automation, power distribution, and mechanical equipment.
Understanding their working principles and mastering the correct installation and wiring methods is a valuable and essential skill for any electrical engineer, technician, or enthusiast, and is a crucial part of building safe and reliable electrical systems.